Cart
Sub-Total: $0.00


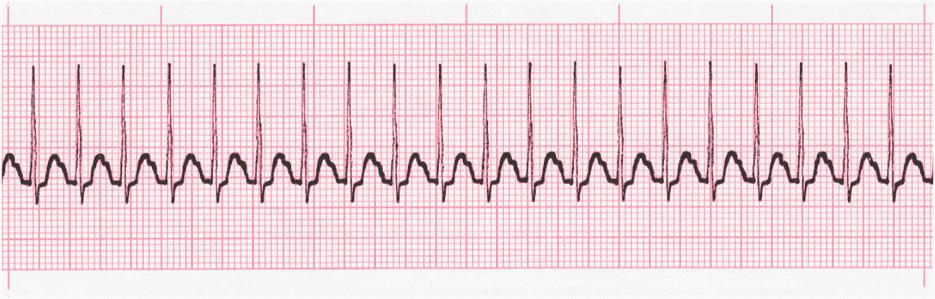
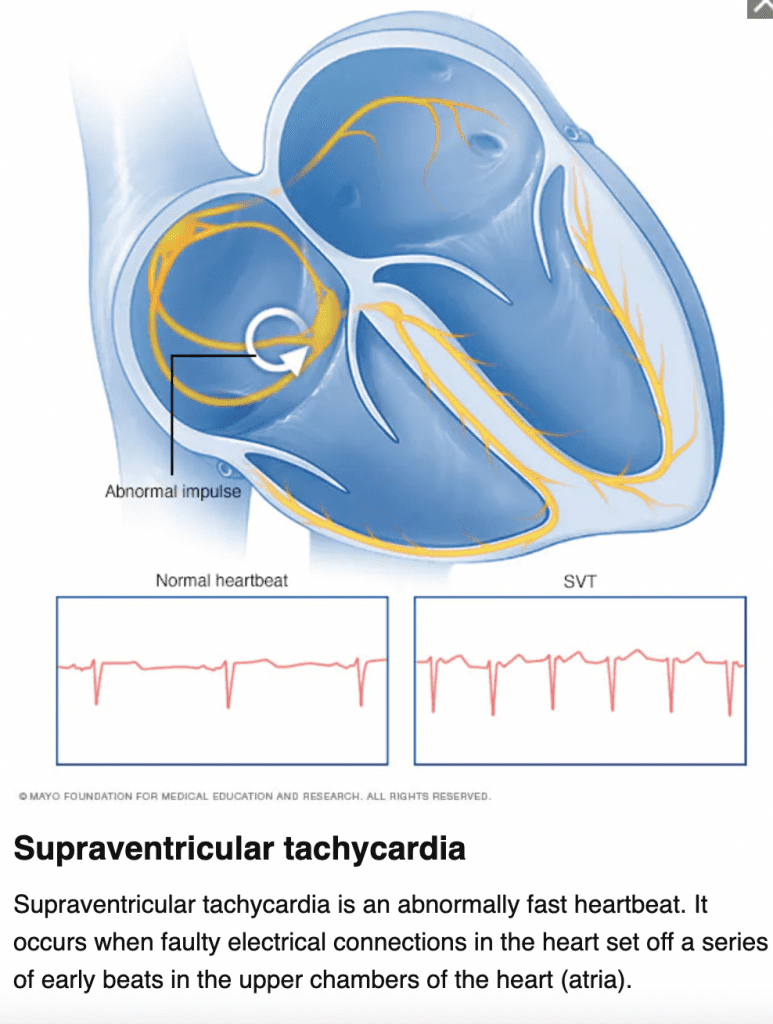
| Characteristics | HR >150, P waves often hidden |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, racing heart, weakness, fatigue, SOB, diaphoretic |
| Treatments | Vagal maneuvers, Adenosine 6 mg IVP (1st dose) 12 mg IVP (2nd dose), Synchronized Cardioversion (low energy shock sync with R wave, not the same as AED mode/Defibrillation which is unsynchronized. Beta-blocker/Calcium Channel Blocker can be used as treatment and expert consultation |


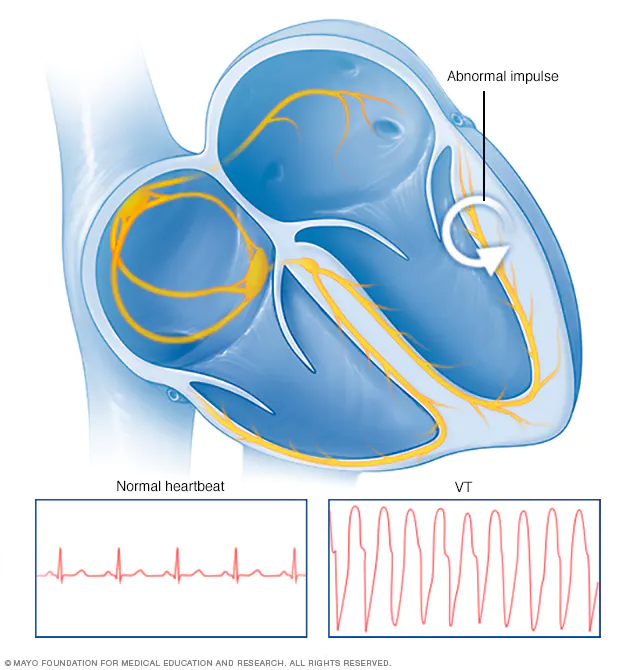
| Characteristics | pulseless VT, can be monomorphic (all examples above) or polymorphic (torsades) |
| Symptoms | Dizziness, SOB, Chest pain, potential cardiac arrest |
| Treatments | 1. Administer defibrillation shock 2. Continue CPR for 2 minutes 3. Defibrillation Shock again 4. Continue CPR for 2 more minutes 5. Administer Epinephrine 1 mg every 3-5 mins/consider advanced airway 6. Administer 3rd shock 7. Continue CPR for 2 more minutes 8. Administer Amiodarone 300 mg IVP 1st dose, 150 mg 2nd dose (alternative to Amiodarone is Lidocaine 1mg/kg 1st dose 0.5-0.75 mg/kg 2nd dose. You cannot give both Amiodarone and Lidocaine, choose one or the other) |
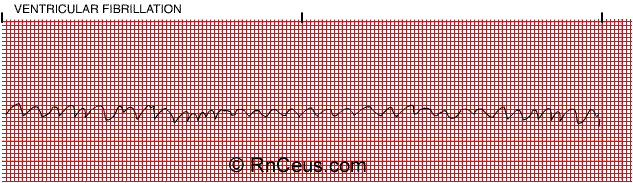
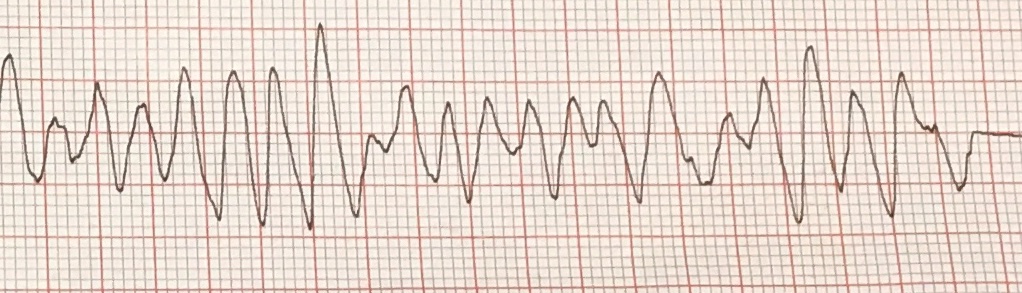

| Characteristics | pulseless VF, rapid/irregular electrical signals cause the ventricles to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood |
| Symptoms | Unresponsive no pulse or breathing |
| Treatments | 1. Administer defibrillation shock 2. Continue CPR for 2 minutes 3. Defibrillation shock higher energy level again 4. Continue CPR for 2 more minutes 5. Administer Epinephrine 1 mg every 3-5 mins/consider advanced airway 6. Administer 3rd shock higher energy level 7. Continue CPR for 2 more minutes 8. Administer Amiodarone 300 mg IVP 1st dose, 150 mg 2nd dose (alternative to Amiodarone is Lidocaine 1mg/kg 1st dose 0.5-0.75 mg/kg 2nd dose. You cannot give both Amiodarone and Lidocaine, choose one or the other) |


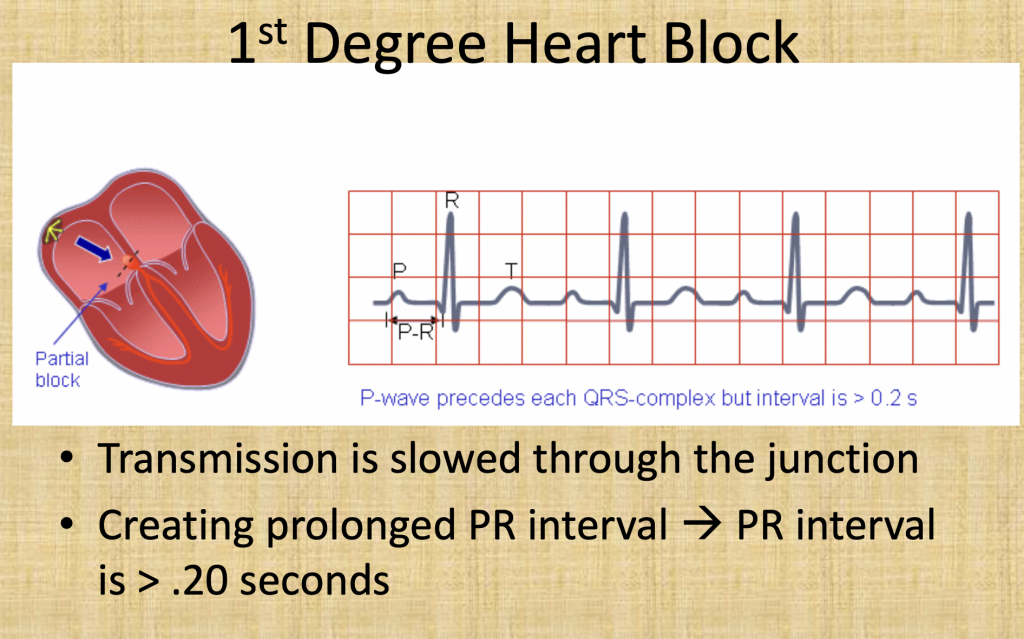
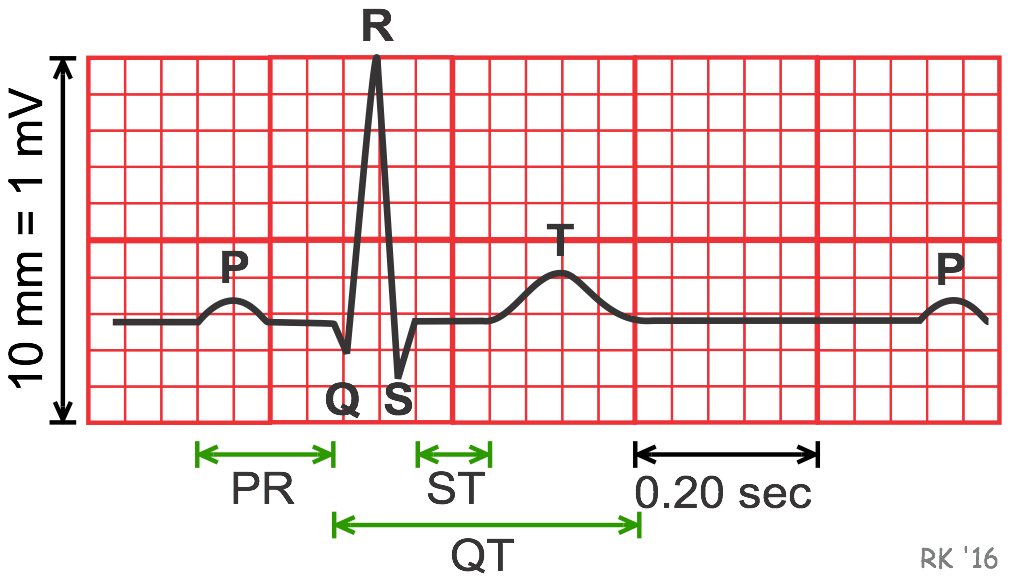
| Characteristics | First-degree heart block is a condition in which the wiring of the heart is slow to send electrical signals but all of the signals are able to pass successfully. There is no electrical block but rather a slowing or delay of the signal Prolonged PR interval |
| Symptoms | No symptoms at times, SOB, chest pain, weakness/dizzy |
| Treatments | 1. Oxygen administration 2. Cardiac monitors 3. 12 Lead ECG 4. IV access 5. If symptomatic consider administration of Atropine 1 mg IV every 3-5 minutes with a max of 3 doses total (3 mg total) Other treatments -Dopamine 5-20 mcg/kg/min infusion -Epinephrine 2-10 mcg/min infusion -Transcutaneous Pacing 60-80 beats per min -Expert consultation |
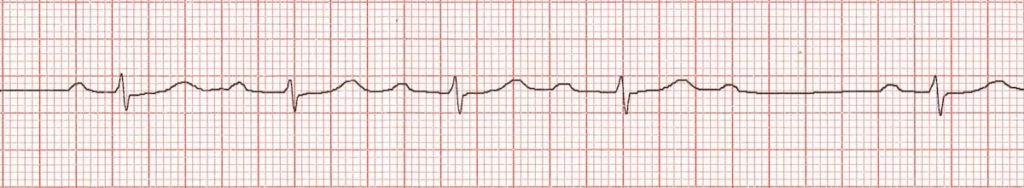
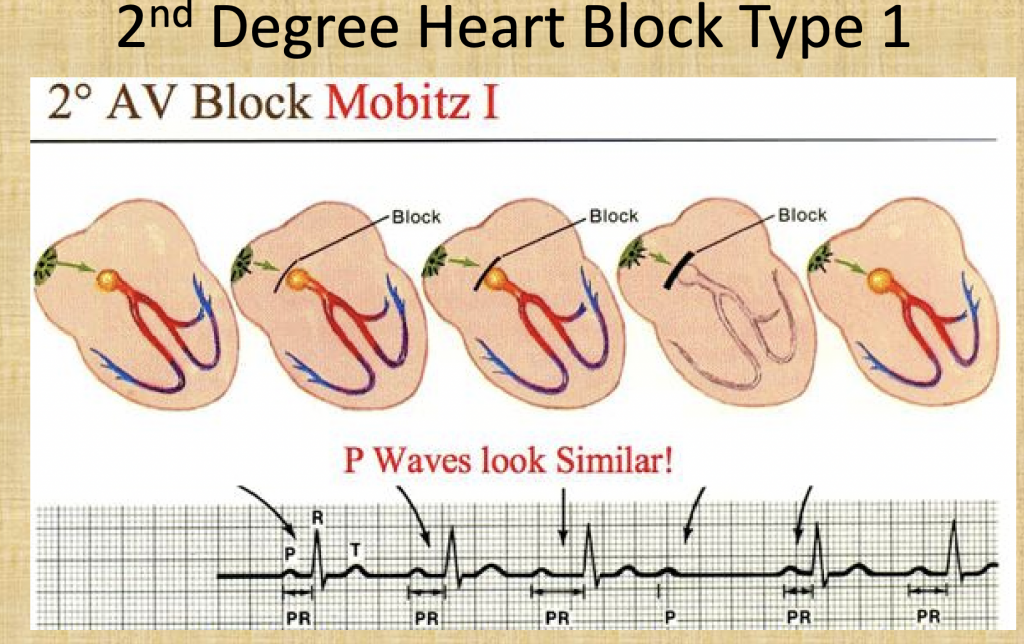
| Characteristics | Second-degree Type 1 heart block is a condition in which transmission of impulse through the AV node is progressively delayed until there is a dropped ventricular beat QRS is staying out longer and longer until it is dropped Causes: Drugs: beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, amiodarone Increased vagal tone (e.g. athletes) Inferior MI Myocarditis Following cardiac surgery (mitral valve repair, Tetralogy of Fallot repair) |
| Symptoms | No symptoms at times, SOB, chest pain, weakness/dizzy |
| Treatments | 1. Oxygen administration 2. Cardiac monitors 3. 12 Lead ECG 4. IV access 5. If symptomatic consider administration of Atropine 1 mg IV every 3-5 minutes with a max of 3 doses total (3 mg total) Other treatments -Dopamine 5-20 mcg/kg/min infusion -Epinephrine 2-10 mcg/min infusion -Transcutaneous Pacing 60-80 beats per min -Expert consultation |

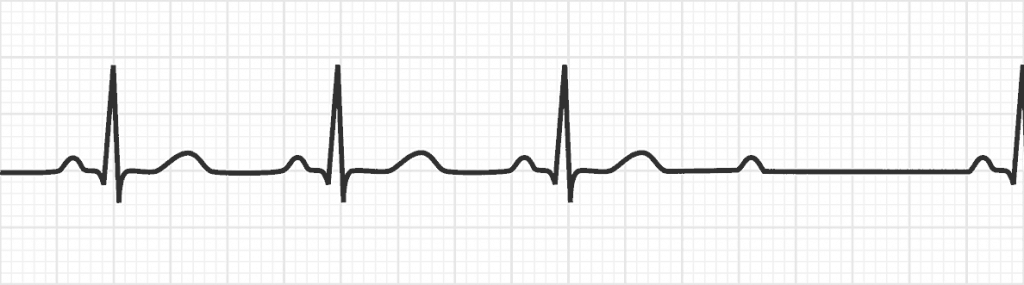
| Characteristics | Second-degree Type 2 heart block is a condition in which is related to structural damage (ischemia) causing a failure of the conduction system at or below the Bundle of His • Narrow QRS = block is within the Bundle of His (approx. 25%) • Wide QRS = block is distal to the Bundle of His |
| Symptoms | Will have symptoms-SOB, chest pain, weakness/dizzy |
| Treatments | 1. Oxygen administration 2. Cardiac monitors 3. 12 Lead ECG 4. IV access Do not rely on Atropine to fix issue! Transcutaneous pacing first line of treatment or Beta Adrenergic medications (epi/dopamine gtt) Other treatments -Dopamine 5-20 mcg/kg/min infusion -Epinephrine 2-10 mcg/min infusion -Transcutaneous Pacing 60-80 beats per min -Expert consultation |
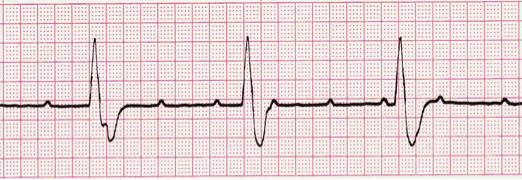
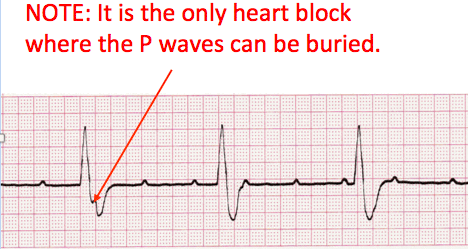
| Characteristics | 3rd heart block is a condition in which there is a complete absence of AV conduction, with none of the supraventricular impulses conducted to the ventricles |
| Symptoms | High risk of ventricular standstill and sudden cardiac death They require urgent admission for cardiac monitoring, backup temporary pacing and usually insertion of a permanent pacemaker |
| Treatments | 1. Oxygen administration 2. Cardiac monitors 3. 12 Lead ECG 4. IV access Do not rely on Atropine to fix issue! Transcutaneous pacing first line of treatment or Beta Adrenergic medications (epi/dopamine gtt) Other treatments -Dopamine 5-20 mcg/kg/min infusion -Epinephrine 2-10 mcg/min infusion -Transcutaneous Pacing 60-80 beats per min -Expert consultation |
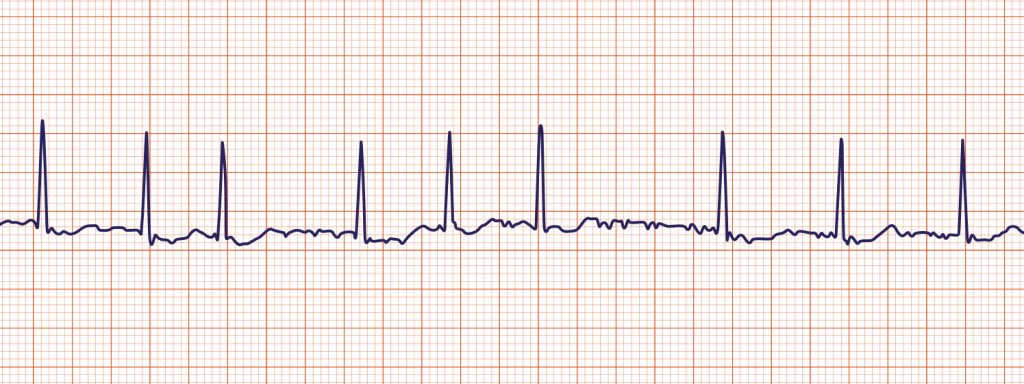

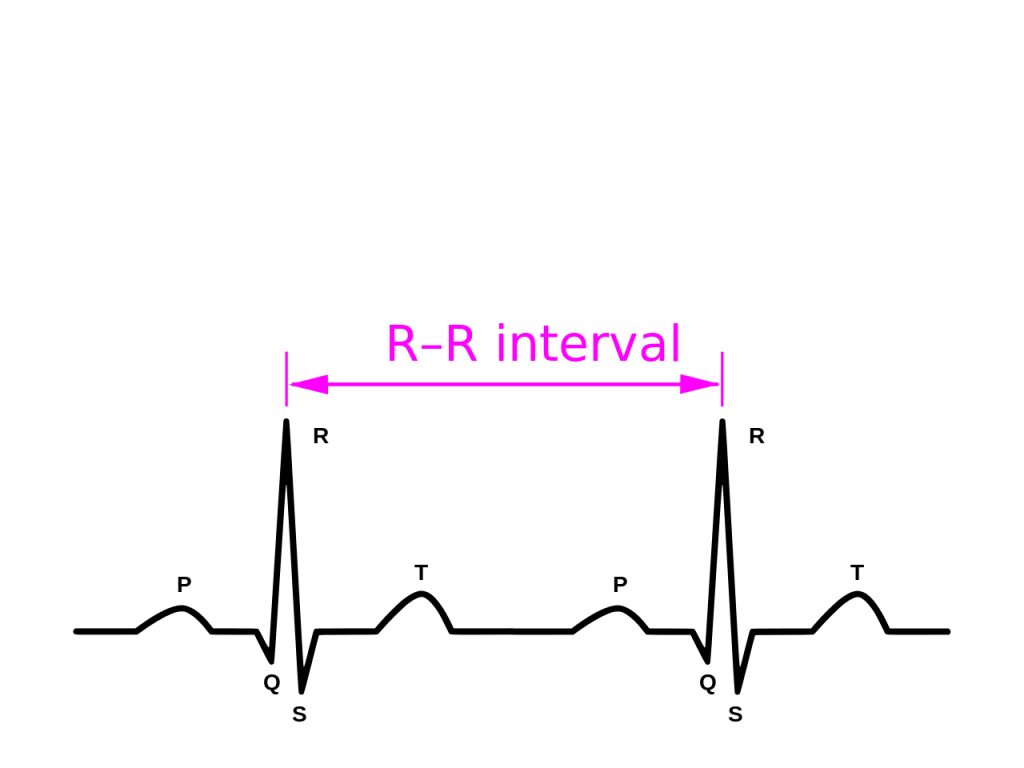
| Characteristics | Upper chambers (the atria) beat chaotically and irregularly — out of sync with the lower chambers (the ventricles) of the heart. Blood is more likely to clot can result in stroke or PE |
| Symptoms | No symptoms or can cause palpitations, SOB, weakness |
| Treatments | 1. Oxygen administration 2. Cardiac monitors 3. 12 Lead ECG 4. IV access Medications: Rate control (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin) Antiarrhythmic drugs (procainamide, amiodarone) Anticoagulants (Coumadin) Synchronized cardioversion |
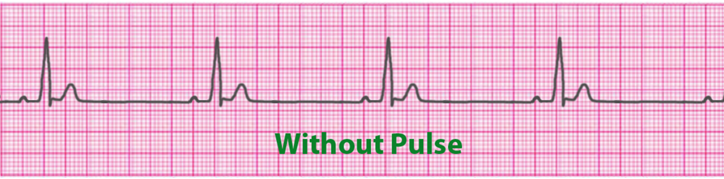


| Characteristics | PEA patient is unresponsive and has NO palpable pulse in the presence of organized cardiac electrical activity |
| Symptoms | Cardiac arrest no pulse, no breathing |
| Treatments | Start CPR immediatley! No pulse so we must adminster Epinepherine 1 mg IV push every 3-5 minutes This is not a shockable rhythm! Our only treatments are CPR + Epi Reversible causes H’s and T’s Hydrogen Ions (Acidosis) Hypothermia Hypovolemia Hypoxia Hypoglycemia Hyperkalemia/Hypokalemia Tamponade Tension Pneumothorax Toxins Thrombosis Pulmonary Thrombosis Cardiac |